How to Find Digital Footprint? Expert Email Tracing Guide
As we learnt all about what is digital footprint and why it is important in cyber forensics in our very detailed last guide. Now, in this thorough blog, we will learn how to find digital footprints in emails using an advanced technique.
Table of Contents
If you want to understand how to track your digital footprint inside emails, the most reliable approach is to simply analyze email header, metadata, server hops, and account activity using a dedicated Email Forensics Software.
While tracing evidence in emails, we’re referring to the complete trail a message leaves behind, i.e how to trace an email, timestamps, IP analysis, authentication checks, and subtle fingerprints hidden in MIME header. These traces help you verify whether an email is legitimate, manipulated, or part of a larger attack pattern. This guide will focus on how to assess digital footprint. So, quickly apply these digital forensics techniques in real investigations and learn the complete process of how to find digital footprint step by step.
Why are Emails the Best Starting Point to Trace Digital Footprint?
When people search for how to look up a digital footprint, they often think of social media or data brokers first. But, in real digital forensics work, email is usually the most revealing starting point. Every email of user carries a detailed set of clues that can help you track user’s online activity, identity, like find PAN card number, technical environment, and link analysis. These are the traces that aren’t visible on the surface. They live inside the metadata, routing paths and email verification records that email servers quietly generate.
This is where MailXaminer becomes incredibly valuable. Instead of manually digging into the manual ways, you can load entire email accounts or exported mailbox files and let the software automatically extract, normalize, and visualize the hidden digital footprints.
Email footprints matter because attackers rarely hide every trace. A forged sender name may still reveal a genuine IP hop. A suspicious domain might still expose DNS infrastructure. A fabricated header might break DKIM or SPF alignment. These tiny inconsistencies help investigators to discover how to find digital footprint more accurately.
Let’s see a practical and reliable way to track your digital footprint or investigate someone else’s email activity. Let’s move into the exact workflow you’ll use.
Extract and Prepare Email Data for Digital Footprint Analysis
You need a clean, complete forensic digital evidence management of data before you know how to trace digital footprint in emails. Many user search for how to find digital footprint inside their email accounts. But the biggest mistake they make is relying only on what their email client shows. Outlook, Gmail, and other mobile apps hide a significant portion of the metadata you actually need for proper tagging and labeling of evidence. That is the reason in digital forensics, the first step is always extracting the full mailbox data and preparing it for forensic analysis.
Through this advanced Spam Email Analyzer, you can load emails in several ways depending on your case:
- Add entire account directly through IMAP or cloud authentication.
- You will get the different email clients to import exported files like PST, OST, MBOX, or EML etc.
- Load different emails from the user’s mailbox added into the software as an evidence.
- Simply trace digital footprint in emails using the advanced extraction feature.
After loading the mailbox, this software automatically normalizes the structure so you see everything the sender and server left behind with no filter, no trimming, and no data loss. This matters because hidden email artifacts such as routing information, intermediary servers, sources IP and MIME attributes are often buried under the full header set.
After loading the mailbox, the next step is organizing the data. The software groups emails by sender, domain, forensic keyword search, timeline analysis, how to identify location from photo, and communication patterns. This organization is crucial when you’re trying to:
- Track your digital footprint across multiple accounts
- Identify suspicious email attachment or senders
- Compare legitimate communication vs. email spoofing
- Map where the data originated and how it traveled

This preparation step sets the foundation for a precise and reliable digital footprint investigation.
Find your Digital Footprint and Analyze the Email Data
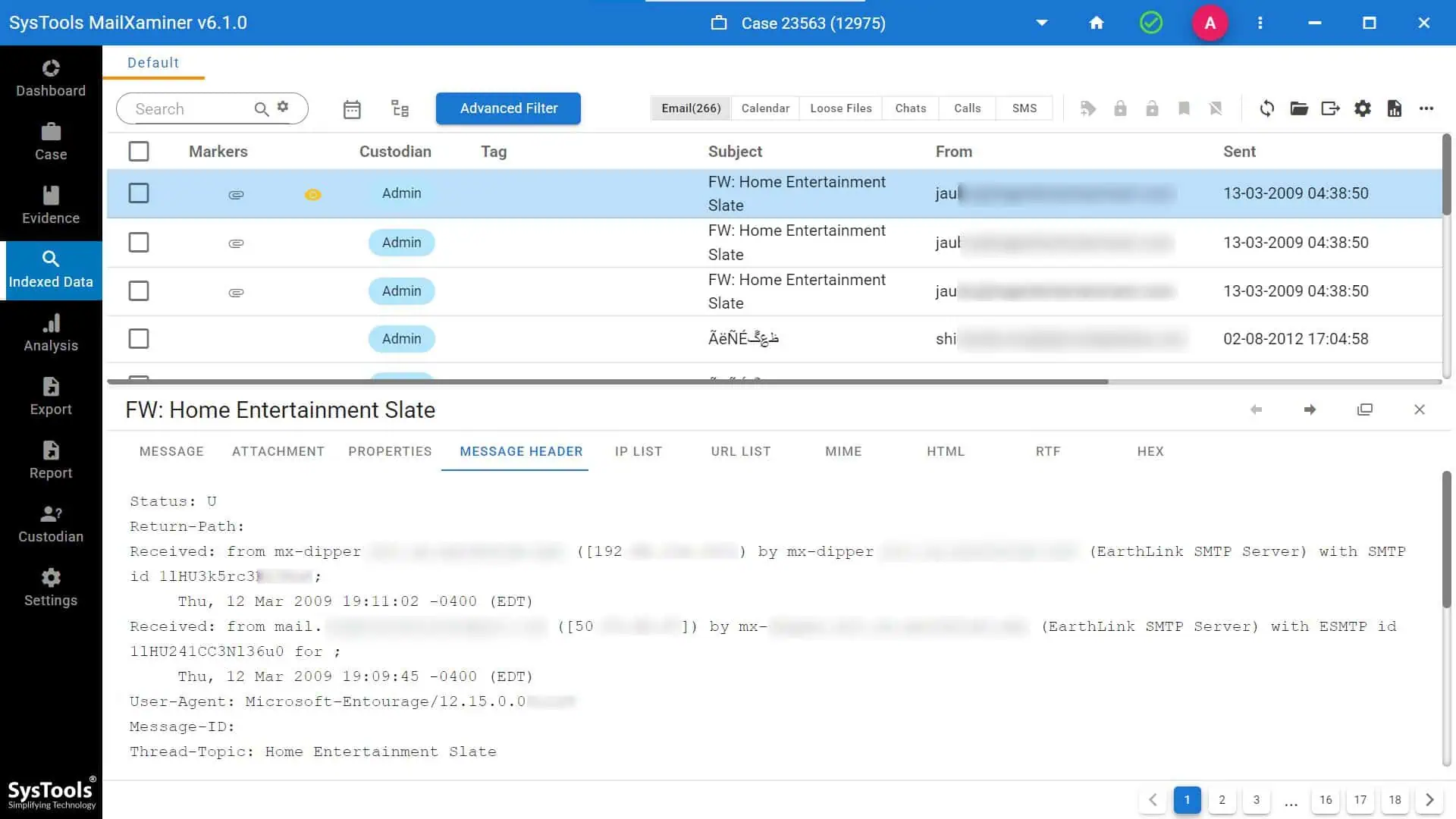
After your email data is loaded and uploaded into the software, the next most important step is in how to find digital footprint inside emails is examining the email clients, like analyze Outlook email. This is the DNA of an email, as it can simply reveal all the properties of an email. But reading and analyzing them manually can be very challenging especially when you are dealing with hundreds or thousands of emails.
This is where our software simplifies the process. Instead of scrolling through blocks of raw header text, the tool extracts and displays every critical element in a structured format. With a single click, you can view:
- “Received” chain- Detailed server hops that show the path an email took
- Origin IP address- Often the most valuable clue in footprint tracking
- SPF, DKIM, DMARC results- Helps detect spoofing or manipulation
- MIME structure- Reveals attachments, embedded objects, and hidden content
- User agents & device identifiers- Useful for linking accounts to the same device
How Investigators Find Digital Footprints in Email?
As we said, to know how to find digital footprint isn’t about checking the browsing history or social media activity. In forensic interrogations, experts use various structured methods and specialized tools to identify phishing emails or suspicious emails, including what type of email exchanges and everything related to the same. Here’s how investigators typically identify digital footprints:
| Section | Description | Key Digital Footprints Identified |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Examining Device Activity | Devices like laptops, mobiles, and tablets store timestamps, logs, and system events that help investigators build a timeline of user activity. | • Login / Logout records • File creation & modification times • Browser history • Application usage patterns |
| 2. Analyzing Network Logs | Network logs capture device connections, traffic flow, and access timestamps that help validate where and how a device connected. | • Router logs • Firewall logs • Server access logs • IP connection & transfer timestamps |
| 3. Reviewing Online Accounts | Email, cloud storage, and social platforms store activity logs that often link a person to an action, even if files were deleted locally. | • Login IPs • Session tokens • Recovery emails • Sent/received messages |
| 4. Metadata Extraction | Metadata stored in files helps verify authenticity, track edits, and identify manipulation or location details. | • EXIF data in images • Document author details • Editing timestamps • Geolocation image mapping |
| 5. Using Specialized Digital Forensics Tools | Forensic tools automate extraction and correlation of email-related digital footprints for deeper insights. | • Sender/receiver metadata • Email routing paths • Header details • Attachment properties |
| 6. Correlating Multiple Sources | Strong forensic conclusions are drawn by correlating data from devices, networks, cloud services, and third-party platforms. | • Device logs • Cloud activity • Network traffic logs • Third-party platform traces |
Conclusion
Your digital footprint is more visible, permanent, and powerful than ever. Every email you send, every link you click, every service you sign up for—everything leaves a trace. For everyday users, this might seem overwhelming. For investigators, it’s a goldmine of evidence. But for the daily user, the key takeaway is simple:
And you can’t protect what you don’t track.
Through this guide, we try to make it clear how to trace digital footprint using the best method across devices, accounts, and especially emails. You also know why modern investigations rely heavily on metadata, headers, timestamps, authentication records, and login activity. But its become very important for every citizen who has linked themselves with digitalization to understand that the process is only half the work, using the right tools is what truly empowers you.

