Email Verification Records in Cyber Forensics: A Complete Guide for Investigators
Email verification records are essential in cyber forensics. This is so because they help forensic investigators to authenticate senders, trace IP sender IP address of emails and detect spoofing attempts. These are the records which help examiners to act a digital footprints and allow forensic analysts to verify whether an email truly came from who it claims to be.
In the world of cyber forensics, emails play a major key evidence in both criminal as well as civil investigations. Tracing the authentication of email communications is crucial for connecting the dots between the criminals, whether it is to identify phishing email attacks, business email compromise, or any kind of data breach. This is where email authentication protocols like SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) come into action. These protocols are the backbone of the email verification process that offers clear, verifiable data that any forensic analyst can examine.
Email verification records also contribute to timeline analysis in digital forensics. If it is handled properly, then it can provide a significant amount of evidence in cases. Also, it helps in maintaining the integrity of evidence that supports a strong case, whether in court or internal investigations. In this cyber forensics, it is important to understand how these records work and what they reveal is a must for anyone in cybersecurity or digital forensics.
Understanding of Email Authentication Protocols in Detail
When any email lands in our inbox, how do we know who sent it?
So, in cyber forensics, that’s not just a curiosity but a critical question. Email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC form the foundation for verification records in cyber forensics. These records help investigators determine if a message was truly sent by the claimed domain or if it’s part of a spoofing attempt.
Let’s break these protocols down:
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
These cryptographic signatures verify that an email hasn’t been altered in transit. It ensures the integrity and authenticity of the message. From the forensic standpoint it is a valid DKIM signature adds credibility to the message’s content that is essential in evidence validation.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
It is like a whitelist of IP addresses that allows sending emails on behalf of a domain. When an email arrives, the receiving server checks if the sending IP is listed in the domain’s SPF record. If it’s not, then the message is flagged as suspicious. For forensic experts, this is often the first sign of a spoofed email.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance)
DMARC ties SPF and DKIM together. It instructs the receiving mail servers on how to handle emails that fail authentication. More importantly for digital forensics investigators, DMARC provides reporting features that log failed authentication attempts that creating a trail of data useful for ongoing investigations.
ARC (Authenticated Received Chain)
ARC is the new kid on the block and incredibly useful in complex email flows, especially with forwarding services like mailing lists. It creates a verifiable chain of trust by recording each server’s authentication results. Forensic investigators use ARC to validate the entire path the email took, ensuring it hasn’t been altered along the way.
Together, these protocols serve as the backbone of email authentication. In cyber forensics, they offer reliable, traceable data that helps investigators confirm whether an email is legitimate, altered, or entirely fake.
Some Other Verification Records
- Headers- Email Header analysis is an important in the digital forensic investigation technique that includes critical metadata like sender and recipient addresses, timestamps, IP address, and the full routing path. This helps build an original trail.
- IP Addresses- A sender’s IP can pinpoint where an email originated, which is crucial for attribution and identifying malicious sources through IP address criminal investigation.
- Message IDs- Unique identifiers like Message-ID forensics or Client-ID help track individual emails across systems and detect duplicates or forged threads.
These protocols not only improve email security, but they can also provide a framework and traceability. In forensic investigations, analyzing these records can confirm whether an email message was spoofed or sent legitimately. However, how contradictory it sounds that these seemingly simple DNS records reveal so much about the emails.
Best Way for Email Verification Records in Cyber Forensics
If we say that there is a one platform that can provide you with a complete analysis of your emails thoroughly? Yes, MailXaminer is the one. When it comes to email analysis, this email forensic software comes into action and becomes the first choice of users in cyber forensics.
It can easily extract, preserve, and analyze data without compromising its integrity. This is the most reliable tool for analyzing email verification records in cyber forensics.
Here is one visual for you on how this software views the email verification records.
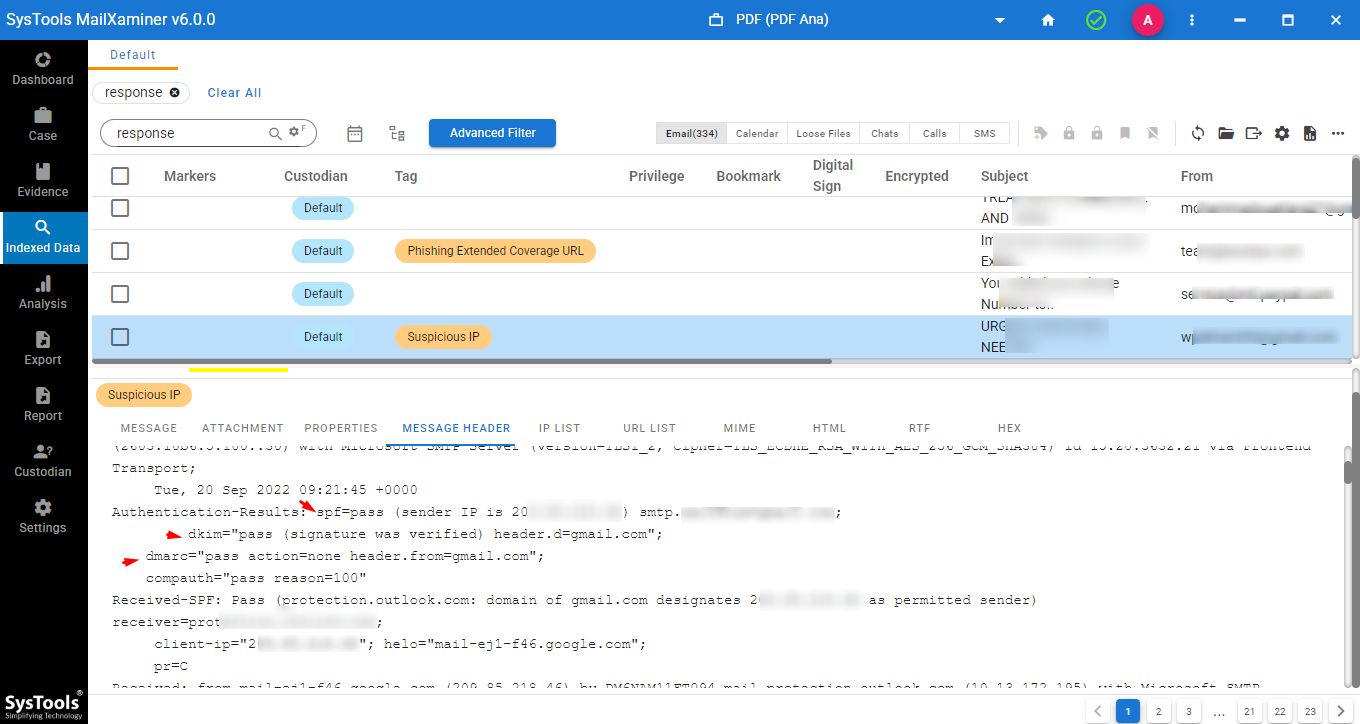
How does This Software Stand Out From Others?
It isn’t just another email viewer. It’s a forensic-grade platform specifically designed for detailed analysis of digital emails. Not only does this support more than 20+ email clients.

It can also process cloud based sources such as Gmail, Office 365, and Yahoo Mail. That makes it a go-to solution in corporate, law enforcement, and legal environments.
This not only sticks to email verification records details only, but also provides various analysis features like link analysis, analyze URL for malware, etc. [Refer to the screenshot below]
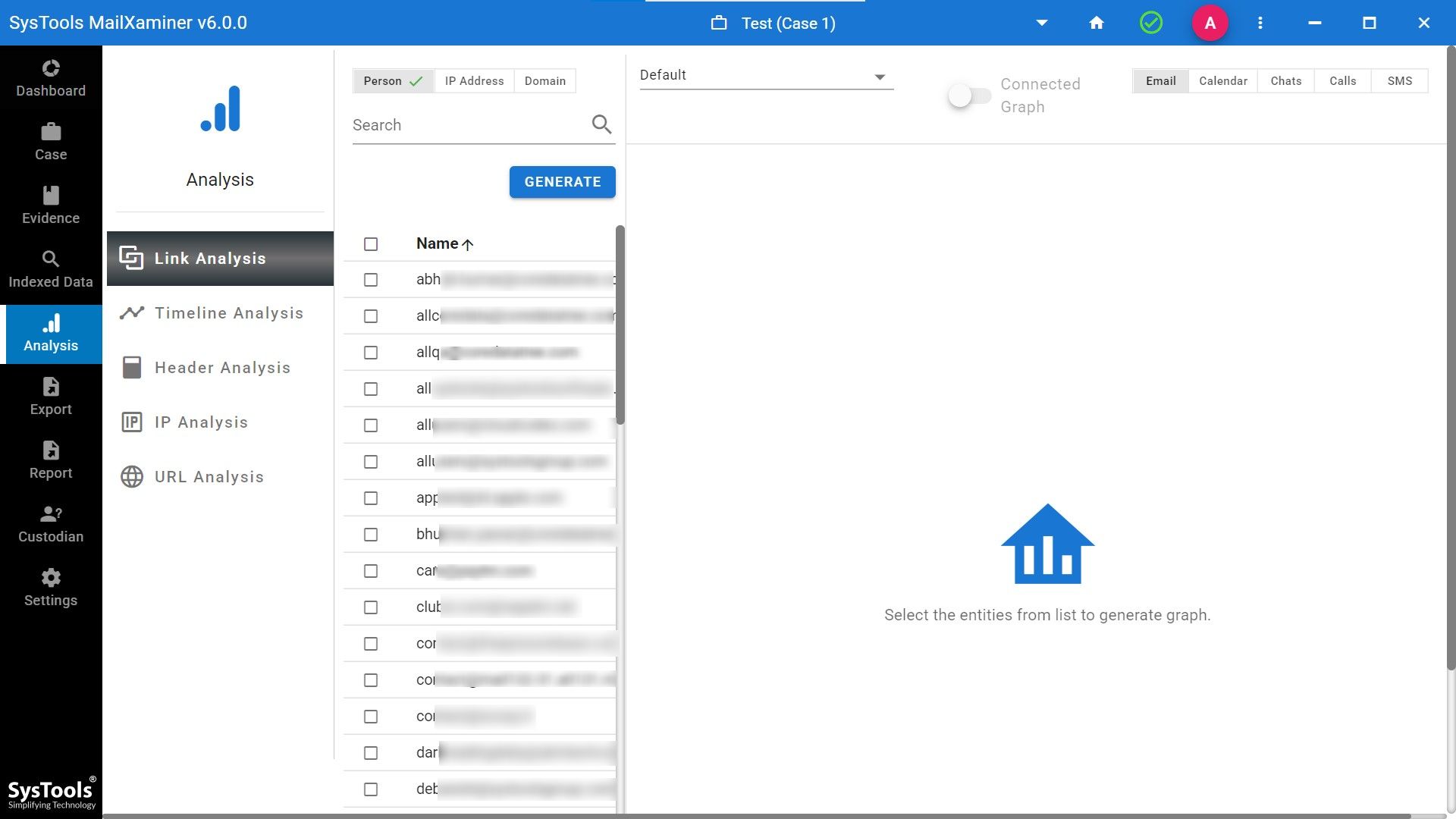
So, whether you’re investigating a phishing campaign, insider threat, or corporate fraud, this advanced, detailed software provides the technical depth and forensic reliability needed to trace and validate email communication without risking data corruption.
Conclusion
Email verification records are one of the most critical components in cyber forensics, offering clear, traceable evidence that supports the authenticity and origin of digital communication. In an age where email spoofing, phishing, and digital impersonation are rampant, understanding protocols like SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and ARC isn’t optional, but it’s essential.
For digital forensics professionals, this software makes it possible to extract, analyze, and present this data in a legally defensible way. From email headers to IP tracing and message IDs, every byte of information helps build a reliable narrative in an investigation.

