What is Digital Evidence Management? A Complete Guide for Investigators
Digital evidence management (DEM) is a structured process and system that helps investigators collect, organize, preserve, and share digital evidence while ensuring it stays authentic and legally admissible.
In simple terms, it’s the backbone that keeps videos, photos, audio recordings, documents, mobile data, and logs reliable enough to stand up in court. A digital evidence management system (DEMS) is a pattern that provides investigators with secure storage, searchable catalogs, and automated audit trails that can protect the chain of custody.
If an investigator ignores the guidelines of the digital evidence management system, then there is a there is high risk of evidence loss, tampering, or inadmissibility. These are the parameters that no investigator can afford during the time of digital forensic investigations.
Meaning of Digital Evidence Management
Digital evidence management refers to both the program of policies and the technology platform that agencies and organizations use to handle the different types of evidence throughout its lifecycle. Evidence can include body-worn camera footage, surveillance videos, photographs, audio interviews, emails, forensic disk images, server logs, or mobile device extractions.
Digital evidence management system (DEMS) supports this process by ingesting the files, metadata analysis process, applying retention rules, securing storage, and producing an auditable chain of custody. In short, DEM protects evidence from the moment investigators collect it until they present it in court, keeping it intact, searchable, and legally defensible.
Why Digital Evidence Management Matters During Digital Forensic Investigations?
Every investigator, whether in law enforcement, corporate security, or cyber forensics, who is involved in any case cannot afford to mishandle evidence. Cases can collapse in court without a defensible digital evidence management process.
- Integrity and admissibility- Courts demand proof that the evidence hasn’t been altered. DEM enforces strict controls in hashing files, logging every access, and preserving the original. So, lawyers and judges can trust its authenticity.
- Audit of digital data- Today’s modern investigations involve terabytes of body-cam videos, IoT data, mobile backups, and cloud logs. Without a structured DEM system, crucial files get buried, misplaced, or duplicated, wasting valuable time.
- Transparency and trust- Agencies face public scrutiny. A reliable DEMS provides secure sharing, audit trails, and disclosure features that increase accountability. Prosecutors, defense teams, and oversight bodies can verify how evidence was handled.
- Operational efficiency- A DEM program streamlines workflows, reduces redundant copying, and speeds disclosure deadlines. Instead of shuffling DVDs or thumb drives, investigators collaborate on a secure platform.
In practice, digital evidence management protects the credibility of the cases, saves the time of an investigator, and reassures courts that justice rests on sound, verifiable proof. For forensic students and experts alike, mastering DEM concepts is now just as important as learning imaging tools or digital forensic investigation techniques.
What are the Core Components of Digital Evidence Management?
It is not a single feature that works for DEM; instead, it’s a combination of processes and systems that work together. Let’s understand what all the main components include:
- Investigators must collect evidence using reliable tools and proper forensic methods. This includes seizing hard drives, exporting emails, pulling data from mobile devices, or capturing CCTV footage. Each step must be documented to preserve the chain of custody.
- The foundation of DEM is secure storage. Investigators back up the evidence in several places, store it in centralized repositories, and encrypt it for security. Storage systems need to be scalable and impenetrable in order to manage increasing amounts of high-resolution files and video.
- DEMS uses metadata, including time, date, location, case ID, and file type, to arrange evidence. This makes it possible for investigators to promptly locate evidence and connect it to the appropriate case.
- Evidence is only useful if it can be understood. DEMS often integrates with forensic tools that allow for keyword searches, metadata analysis, or even AI-based object detection in videos. This speeds up investigations
A combination of all these components provides a complete lifecycle approach to managing digital evidence.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Evidence Management
DEM implementation has drawbacks despite its benefits:
- High data volume: As mobile devices, CCTV, and bodycams become more common, storage needs are rapidly growing.
- Format diversity: Managing various file types, such as server logs or videos, calls for adaptable systems.
- Pressures to comply: Agencies need to stay abreast of evolving forensic standards and privacy laws.
- Budgetary restrictions: Enterprise DEMS and safe, scalable storage can be costly.
- Skill gaps: To use DEMS efficiently and prevent mistakes, staff members require training.
Businesses that ignore these issues run the risk of inefficiencies, noncompliance, and even case dismissals.
Best Practices for Digital Evidence Management
After learning about the challenges, let’s discuss how we can overcome these challenges:
- It is best to establish clear policies for evidence handling in digital forensics.
- This could be a best practice; if you are not sure about your evidence management technique, then you should work only on verified copies.
- Implement strong security measures like encryption, role-based access, and multi-factor authentication.
- Train personnel on DEMS features and legal requirements.
- Adopt retention policies aligned with legal mandates.
- Why not try an all-in-one email forensic software for complete digital evidence management expertly.
How Does this Advanced Digital Evidence Management Software Help?
When it comes to handling digital evidence management, investigators need more than just secure storage; they need intelligent tools to examine data quickly and reliably. MailXaminer empowers forensic teams to manage and analyze digital evidence with precision.
The software accommodates 20+ email file types (e.g., PST, OST, MBOX, EML, NSF), making it widely applicable in cases related to corporate correspondence, deception, or cybercrime.

Investigation teams will not be required to manually filter through emails because they can take advantage of advanced Boolean Operators, analyze email headers, and keyword search filters to filter out the most relevant evidence.
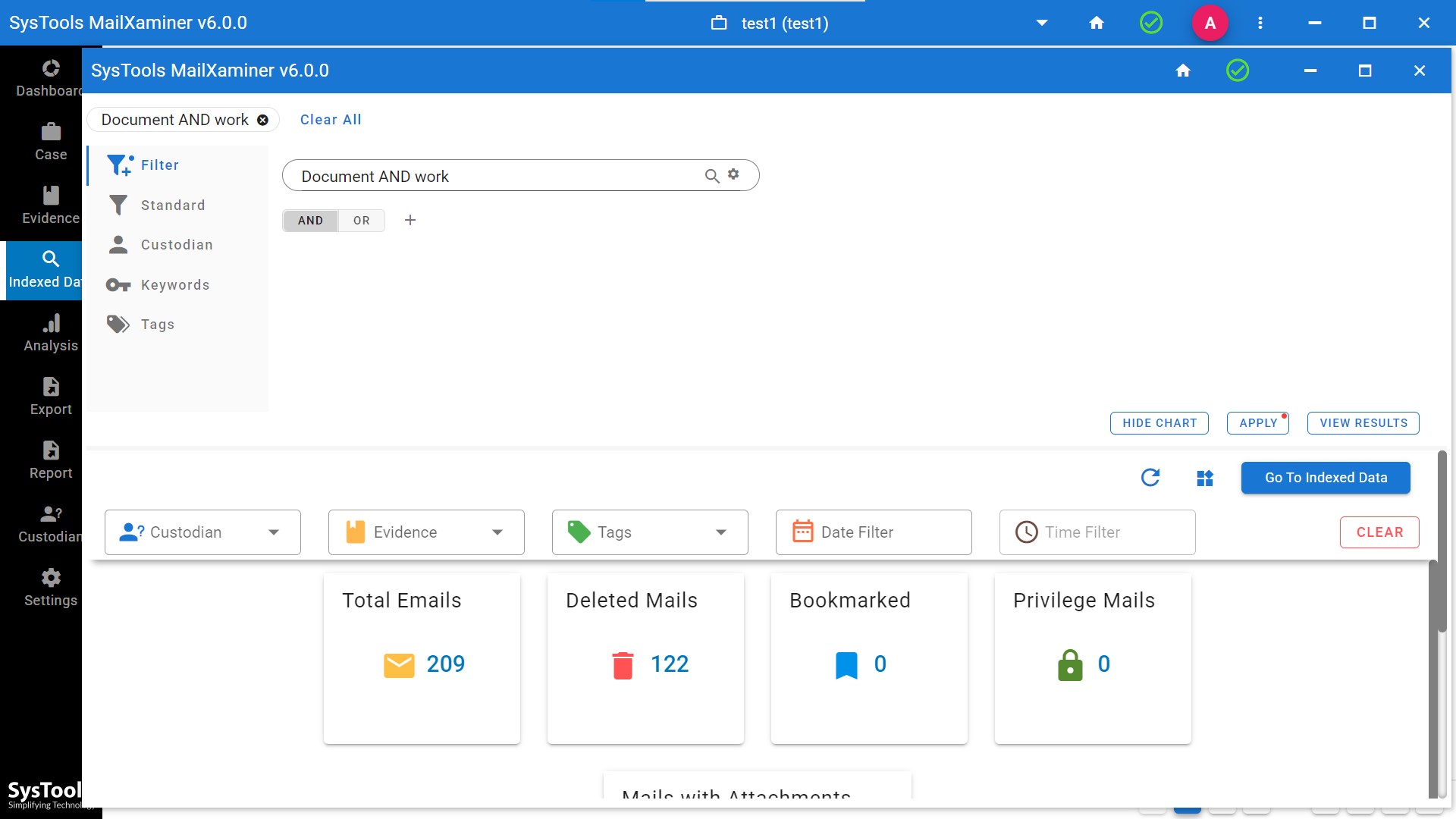
It has a smart case management functionality that allows a case investigator to analyze the evidence in different ways. This software bridges the gap between raw data and court-ready evidence. This makes it an invaluable component of modern digital evidence management strategies.
Conclusion
Digital evidence management is essential for preserving integrity, ensuring compliance, and maintaining the chain of custody in modern investigations. Investigators can transform complicated digital data into trustworthy and court-ready evidence by adhering to best practices and using advanced applications as discussed.
As the amount of evidence increases, strong digital evidence management strategies will continue to be the foundation of reliable and efficient digital forensics.

