What are the Types of Digital Evidence in Cyber Forensics?
Digital forensics is a field that reconstructs cybersecurity events. It can be done by analyzing and preserving digital evidence, such as malware files and malicious scripts, left by threat actors. This helps investigators identify criminals and identify the root causes of crimes. Investigators follow a chain of custody to track, collect, and handle the evidence while making sure no one tampers with it. Courts, insurance companies, and regulators can then use this information during legal cases, claims, or audits.
Investigators rely on digital evidence in most criminal cases because crime-related information is often recorded digitally. Digital forensic investigation techniques for fast and effective gathering, preserving, and securely handling different types of electronic evidence are essential.
Collecting various types of digital footprints is not at all for investigators in today’s world. Today, with knowledge and expertise, an examiner should have highly advanced equipment like software and methodologies.
What are the Different Types of Evidence that Help in Digital Forensics?
To get a better understanding of the handling of essential types of digital evidence during an investigation, let’s go through each of these:
Volatile data
Data that is temporary and the chances of it being lost in the event of a power outage are kept in cache memory or RAM. As it may include important information, it is necessary for forensic investigations into cybercrime.
To avoid data loss, data should be collected as soon as possible, on-site or remotely, and the computer’s current condition should be recorded. To avoid data loss and enable forensic specialists to examine cached data, including webmail, continuous charge is required.
Non-Volatile Data
Digital information that is kept in a particular state after power is cut off and saved in a file system is known as non-volatile data. Examples include account information, audit records, system event logs, configuration/log files, data files, dump files, paging/swap files, temporary/cache files, and hibernation files.
The registry is a database unique to the Windows platform. It is a useful digital resource because of this data and possible proof.
Network Data
A network data model offers a dynamic framework for comprehending the complex web of links inside a system by emphasizing the relationships and interactions between various items.
Fundamentally, a network data model arranges information to represent the innate connections between items.
Mobile data
Digital information includes a variety of data, like multimedia items – images, videos, and audio, and personal data like contacts, calendars, and messages. It may also contain location data, app use statistics, browser history, and other user activity or email verification records.
Cloud data
A platform that links and adds corporate data from many sources, both inside and outside the organisation. It facilitates cooperation and real-time data access that enables businesses to develop and get valuable insights. The business may collect data from mobile apps, e-commerce websites, and physical storefronts using data for cloud forensics.
Information about the Email
Metadata is the information that tells about an element of data or data collection, like the author, creation date, or file size. A data system is enhanced by it. This helps in making it easier to find, arrange, and use data for email metadata analysis. It tells information about data that is different from the actual substance.
Artifacts
Any data that is kept on a digital device and offers insights about how it was used and what was done with it is called an artifact. System logs, browser histories, hidden files, and even the remains of deleted objects are all examples of artifacts, which are more than just files or documents.
In order to solve crimes, conduct audits, or simply verify that company policies are being followed, forensic investigators need these components in order to put together digital evidence.
There are many examples of digital evidence in digital forensics, hence, there is a software to collect evidence from multiple platforms is necessary. MailXaminer helps to store, analyse, and produce advanced reports regarding Email, Network, Cloud, etc.
Advanced Features supporting the application to Trace Different Types of Electronic Evidence
To see, analyze, and investigate the harmful communications between any number of suspects, use the sophisticated link analysis approach. It is incorporated into the application.
This helps the investigators collect different types of digital footprints. This can be examined for the emails and information exchanged, and the suspects’ relationship as soon as possible. Use advanced Boolean Operators for search to find connections between many individuals. Analyze and show their email conversation using the suspicious keywords.
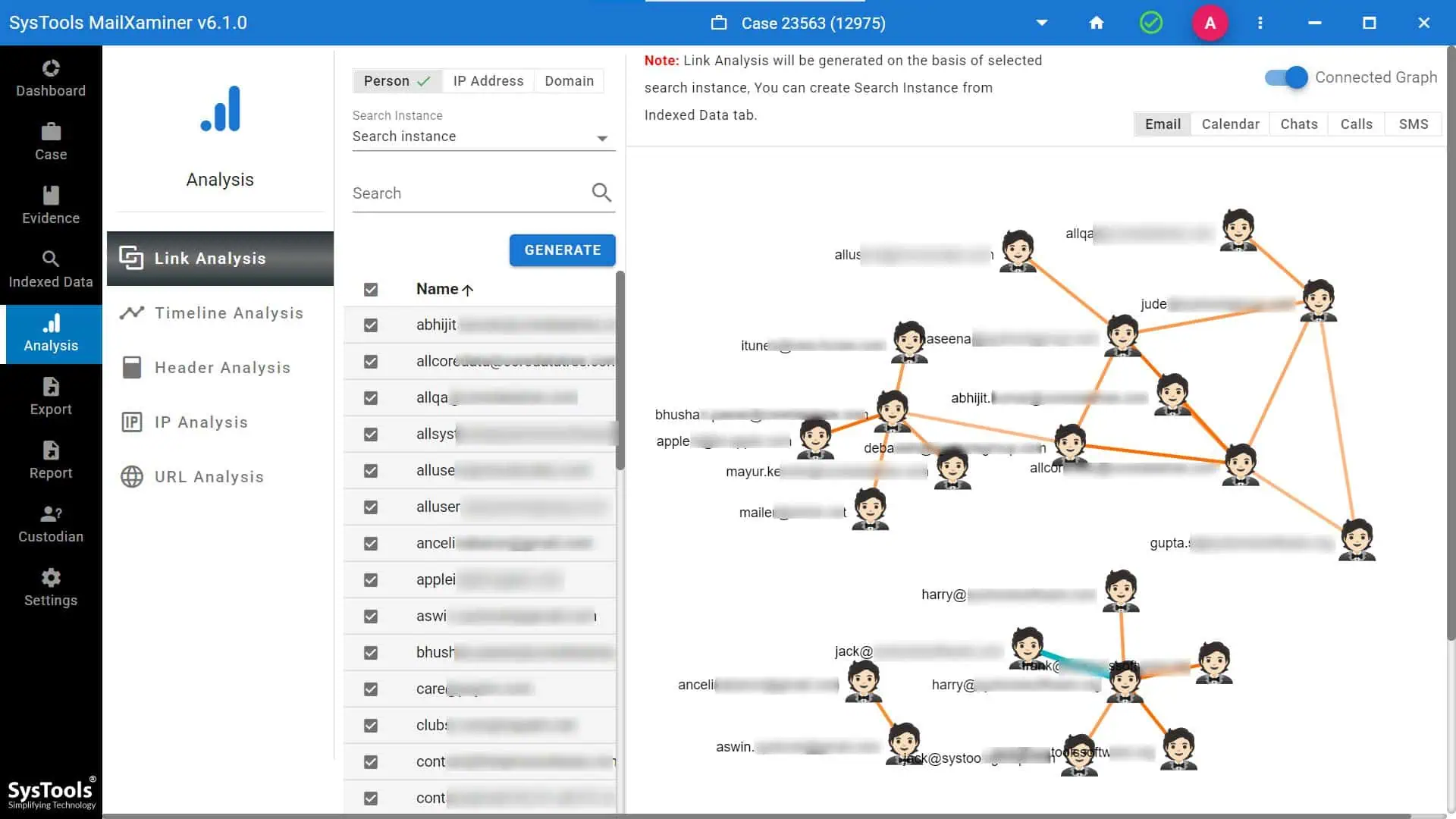
Following the forensics recovery, you may use several operators to look for evidence in the email and contacts body (To, Cc, Bcc, Subject, First Name, Last Name, Sender Name, etc.). One can also look for evidence in suspicious email attachments and eliminate duplicate emails that have been searched.
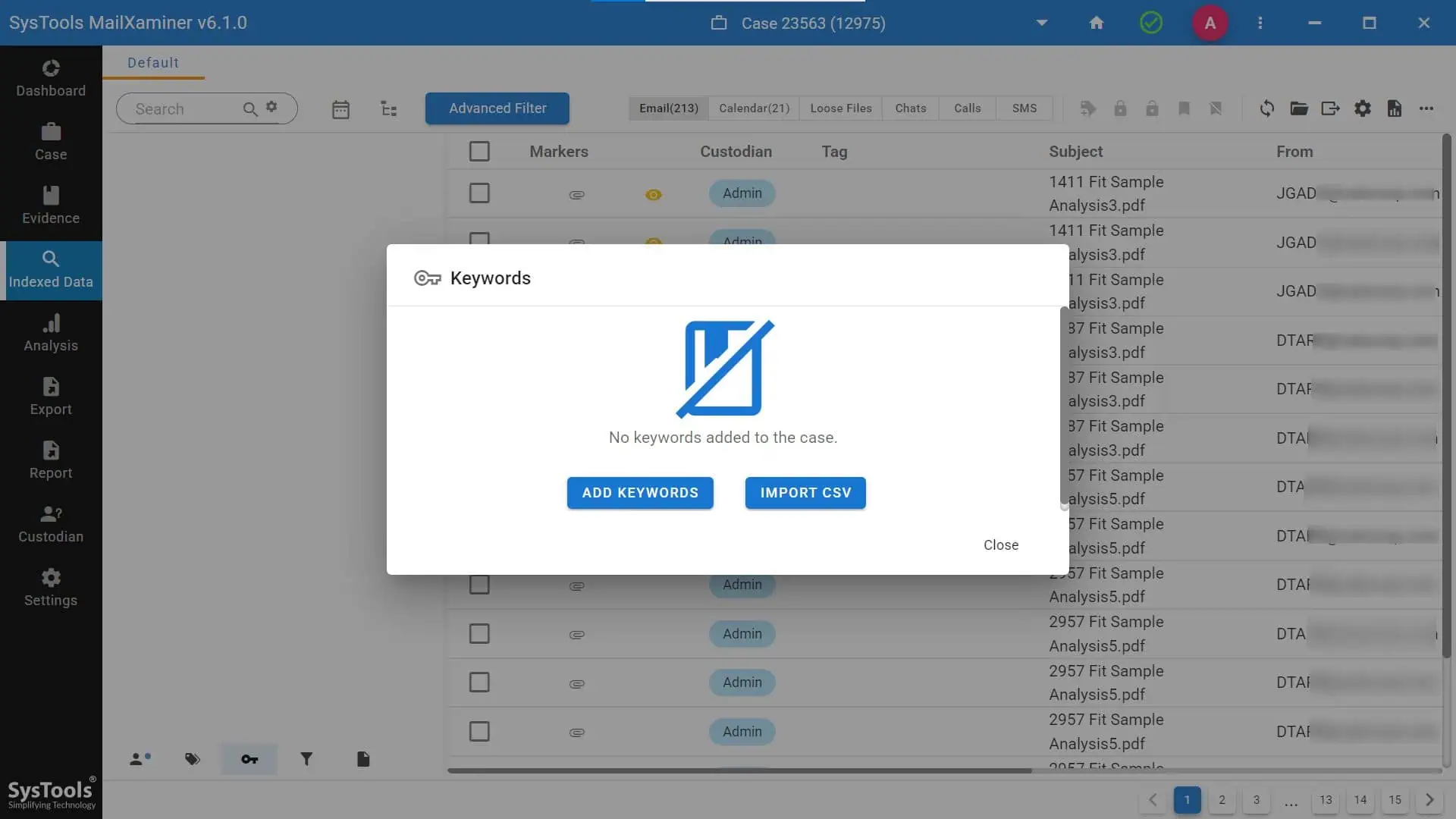
Obtain the list of emails and attachments that include certain suspected case-related keywords. A CSV file containing the list of suspicious terms may be imported, or a variety of forensic keywords can be manually inputted.
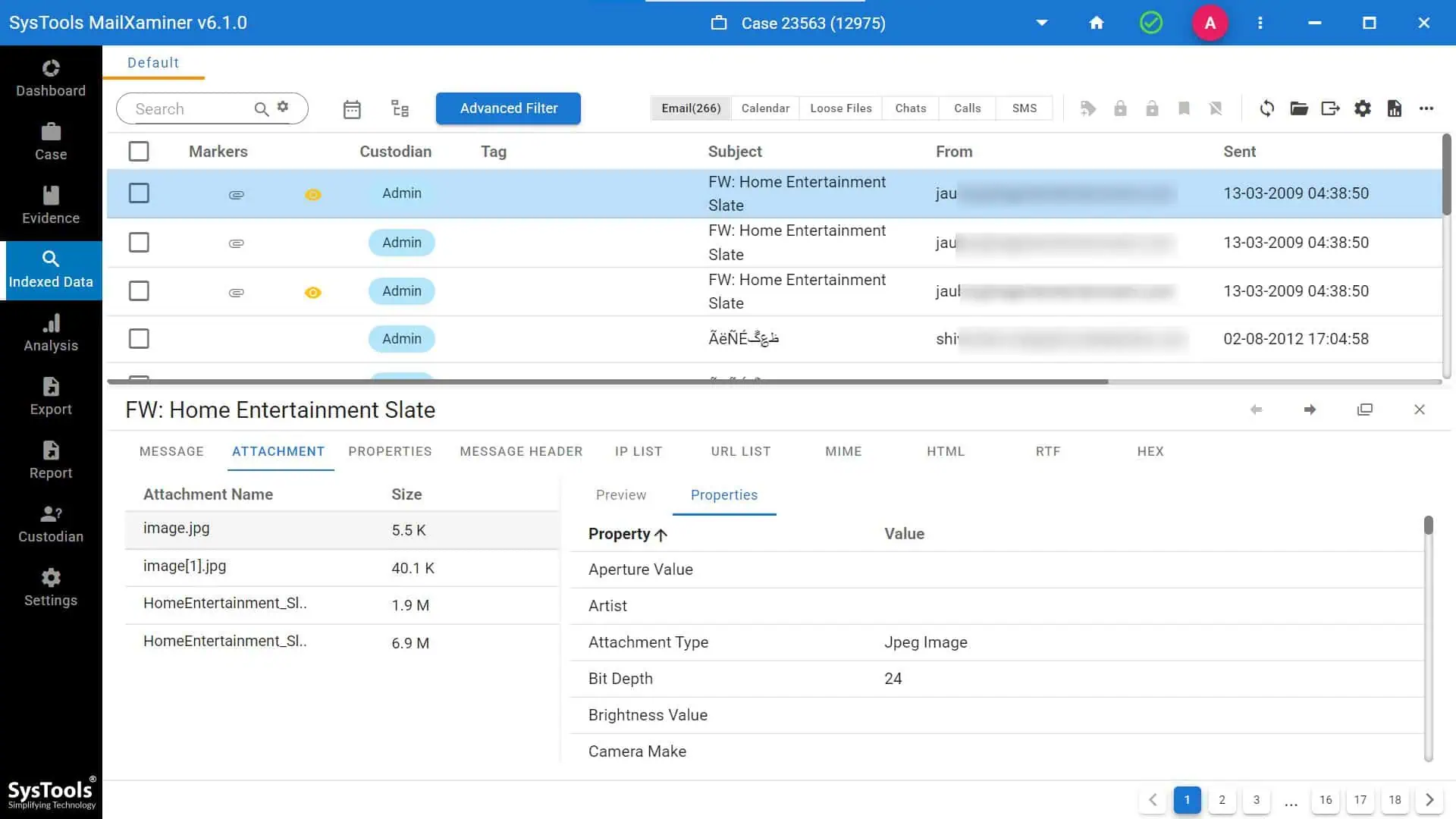
Examine deleted, read, unread, or password-protected emails from a forensic standpoint to get all of the information contained in them. Investigate emails from several perspectives to identify any fabricated or corroborating evidence.
You can examine evidence found in any disk image file by using the enhanced loose file forensics support option. To read files without any issues, experts must verify the Document or Loose file option.
If any evidence files are imported into the program, the OCR setting is used during the investigation. Experts may then review all the information contained in the image file that has been processed using the OCR technique.
Conclusion
Various types of digital evidence in digital forensics include volatile data, nonvolatile data, network data, cloud data, and artifacts. The best email forensic tool can help you collect, analyze, and produce robust reports on Email, Network, and Cloud.
Digital evidence exists in a wide variety of formats and sources. The ability to locate it and present it effectively in court can significantly influence the outcome of a case. It helps to establish or refute a suspect’s role in criminal activity.
Modern digital forensics solutions make it possible to recover nearly all file types. These are even those that appear lost due to deletion, corruption, or overwriting. Having reliable forensic tools available is therefore essential for any investigation.

