Digital Evidence Collection in Cyber Security – All You Need to Know
Cyber security, computer security, or information technology security relates to the protection of computer systems. It deals with protecting digital devices from theft or any kind of damage to electronic data. Cyber security is becoming one of the major challenges in this contemporary world due to increasing reliance on smart devices that constitute the “Internet”, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and other Internet wireless network standards. Hence, there comes a need for digital evidence collection in cyber security.
In today’s time, every person who is using the internet has to face alarming cyber risks. The risk is considered at a higher pace if there is no verified online security at your workstation or home. Life of people are really not safe as they blindly rely on this internet world in different aspects such as shopping email, messaging, social media, etc.
We would suggest that users first know about digital evidence collection & then go through the entire process to get their results. Moreover, it helps users in getting a detailed understanding of the topic.
What is Electronic Evidence in Cyber Forensics?
Digital evidence is the kind of information in binary form which is mainly associated with e-crimes. During cybercrimes, it is the information that is derived from digital devices to get the other pieces of evidence regarding the crime. Hence, the digital evidence collection process is a very crucial operation.
Since computers and mobile phones are mainly used to commit crimes. Hence, one’s mobile phone files or system data can reveal a lot about the intention and workflow of that person. So, law enforcement agencies started to do a forensics investigation of the suspect’s digital devices to investigate the crime scene.
Doing this will help them to implement digital evidence collection in cyber security. Furthermore, to carry out an in-depth investigation for the gathered crucial information, users can make the best use of computer forensics tools.
Digital forensics is the process of identifying digital evidence which is further used by the court of law. It is the science of finding digital evidence within a process to analyze, inspect, identify, and preserve digital evidence associated with electronic devices. It provides the best techniques and tools for the forensic team to resolve complicated digital cases. In a nutshell, such tools are a boon for data evidence collection in the cyber forensic field.
Digital Evidence Collection in Cyber Security – Challenges Faced
Here are some of the major challenges that could be faced by the forensics examiner while collecting the evidence. These are the reasons why experts also want to learn how to collect digital evidence using the latest technology.
- No. of PC and extensive use of internet access can increase the difficulty during the investigation process.
- Tools and software to trace the hacking are not easily available.
- Lack of physical evidence can make the prosecution process difficult. Moreover, evidence may not be present at the actual crime scene but distributed across data centers(on the cloud) in multiple different locations.
- Large storage space in Terabytes can make the examination process vast and difficult.
- Criminals may use methods like stenography to hide relevant info in plain sight, causing investigators to overlook the evidence. Sometimes highly technical culprits may use digital bombs to remotely destroy the evidence before/during or after the collection of digital evidence.
- Must be adaptive to the present situation. For instance, any changes in technology may lead to the up-gradation of certain techniques.
- Increasingly sophisticated encryption (passwords, 2FA, and algorithms like AES-265) designed for privacy are misused by nefarious entities to make data inaccessible.
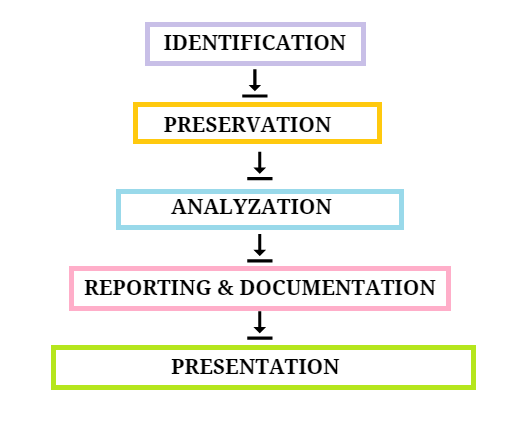
Digital Forensics Process Model
Almost all Digital forensics investigation techniques entail the following steps to gather or handle digital evidence:
- Identification
- Preservation
- Analyzation
- Reporting and Documentation
- Presentation
Let’s Discuss Each One of Them in Detail for Digital Evidence Collection in Cyber Security
1. Identification
- Recognize the purpose of the investigation.
- Identify and collect the resources required in the investigation.
2. Preservation
- Isolate the data files or devices for examination.
- Secure the files to inspect data.
- Preservation of data for investigation.
3. Analysation
- Identify the techniques and tools to use to analyze digital evidence.
- Process data and interpret the possible results.
4. Reporting and Documentation
- Prepare documentation of the complete crime scene.
5. Presentation
- Get a conclusion with the help of gathered facts.
- Summarization and explanation of the process.
Learning how to collect digital evidence is easy when we split the entire task into these five phases. It makes the entire task simplified by arranging the operation in chronological order.
Best Practices Before During and After Digital Evidence Collection
Here is a list of procedures for a criminal investigation having cyber evidence of any kind. These should be followed as they are part of many internationally recognized standards such as ISO, SWEGC, and more.
First up after arriving at a crime scene from where digital evidence may be present is to secure the zone. Then identify and document the evidence in its current state, and take photos, of serial numbers, device status, and wire arrangement. If photo recording is not permissible make sketches instead.
All this documentation is necessary to ensure that digital evidence collection happens soundly.
Isolate the most vulnerable devices to prevent any kind of contamination. This is done by formulating an order of volatility chart. Which generally is as follows
- Registers and Cache
- Memory (RAM)
- Kernel Statistics and System Logs
- Process Table and Running Processes
- ARP Cache and Routing Table
- Temporary File Systems
- Disk
- Remote Logging and Monitoring Data
- Network Topology and Physical Configuration
- Archival Media
Document every aspect of the collection, i.e. keep an answer to who, what, when, where, how, and why of every action in digital and physical media.
This forms the basis of maintaining the most critical aspect of digital evidence collection, which is the chain of custody
Importance of Evidence Gained During the Investigation
In the digital forensic examination process, the most important competency for the one who conducts the investigation is to gather and examine different types of evidence. Experts can gather several types of evidence from digital devices that can help the investigator make wise decisions during the case.
First Rule: If the evidence is not related to the case, then it is not relevant evidence. It must be appropriate to the investigation for the admissibility of the court.
There are many types of evidence that are not admissible to court, but they are valuable for the investigation to reach a conclusion. Some artifacts are even not admissible in their own way, but they may be admissible in conjunction with other evidence.
Advantages of Collecting Digital Evidence in Cyber Security
Below mentioned are some advantages of Digital Evidence Collection in Cyber Security:
- It ensures the integrity of computer systems and other digital devices.
- When producing this evidence in court, the authorities can make the right decision.
- If systems & networks are compromised in an organization then it can help capture important information.
- It helps to track down cybercriminals across the world, efficiently.
- Extract, process, and interpret the evidence in the court, so that it proves the action of the criminal.
Concluding Words
For digital evidence collection in cyber security, the investigator needs to follow a proper procedure that helps to capture the perpetrator. Understanding this blog leads to efficiently recognizing the crime scenario by following the different stages that are incorporated into the digital forensics collection process.
As a result, the gathered evidence is admissible in a court of law. Finally, we can say that the digital evidence collection process is not that tricky if users are aware of the right technique.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Collection of Digital Evidence
Q. How is the collection of digital evidence different from the data acquisition phase of forensics?
Collecting the evidence that is present in a digital format happens after the investigator identifies it. So it involves the physical extraction of devices from the crime scene into the lab. Acquisition on the other hand is a closely related next step in the digital forensics process where a master and working copy of the data on these devices is made.
Q. After identification how is the collection of volatile data from a live digital evidence system?
As volatile data is most easily lost investigators need to use specialized frameworks and make use of inbuilt commands on the systems. If the digital evidence is present in a Windows machine ‘ipconfig’ command can obtain the necessary network information, while on Unix systems, the command is ‘ifconfig’.
Universal ‘netstat’ command can be used to collect the active network connections from any of the computer operating systems.
Other advanced external platforms can perform a more in-depth collection so use them if necessary.
Q. Why is the digital evidence put in a Faraday bag after collection?
A Faraday bag is a container made from a conductive material covering the outside with soft cushioning on the inside. Due to this, it does not allow any external Electromagnetic signal to reach the device. So digital evidence can be safely kept and transported from the crime scene to the lab.

